· tips · 2 min read
Type Wars: The Battle Between typeof and instanceof in JavaScript
A practical, example-driven guide to choosing between typeof and instanceof - learn their differences, pitfalls, cross-realm quirks, and reliable alternatives for robust type checks in JavaScript.
Win the type-checking war: what you’ll gain
You will learn when to reach for typeof, when instanceof is the correct tool, and when both will fail you. You will also get reliable patterns to reduce bugs caused by JavaScript’s type quirks.
Short, actionable. Then deep. Read on.
Quick reference (cheat sheet)
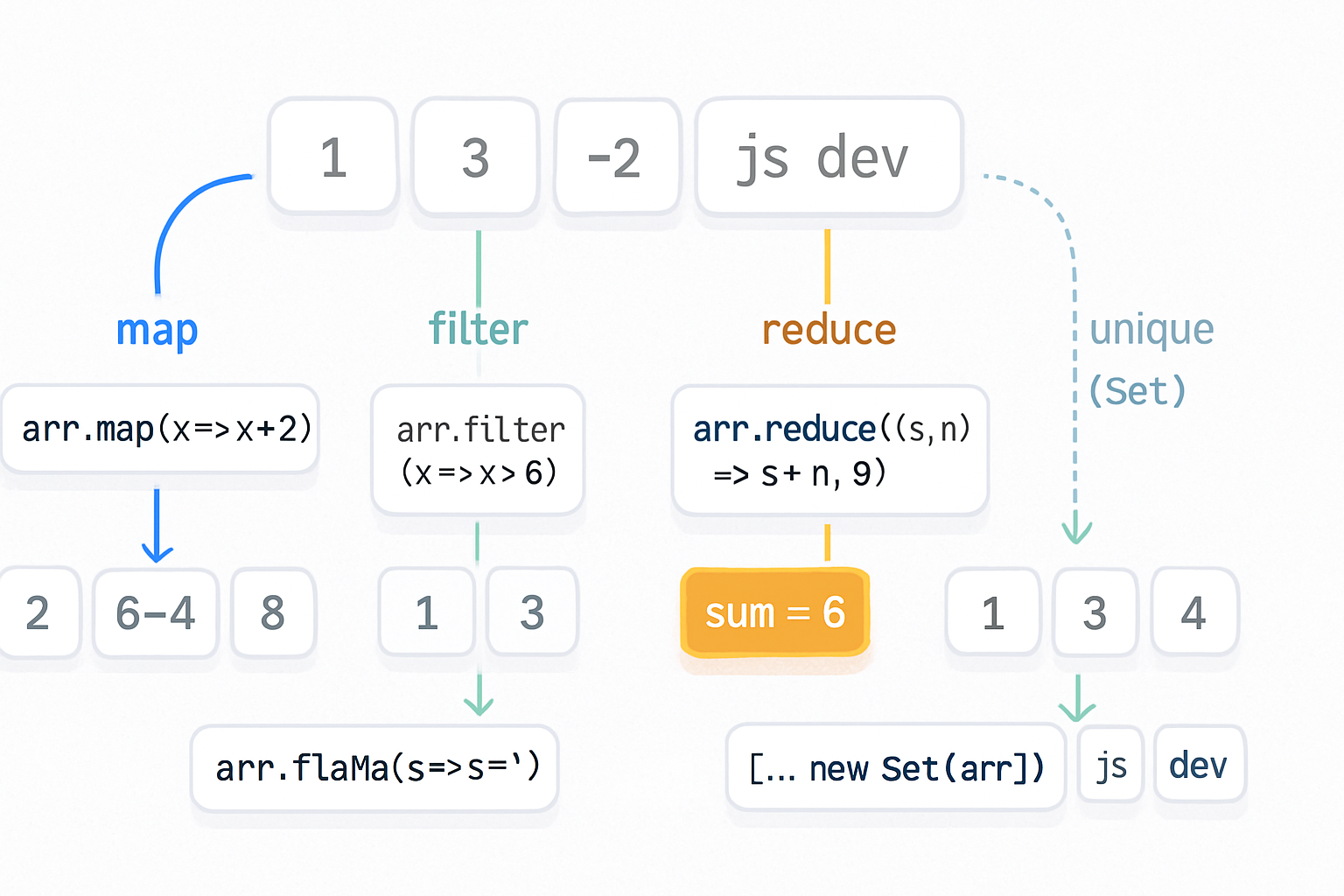
- Use
typeoffor primitive checks (strings, numbers, booleans,undefined,symbol,bigint) and to detect functions. - Use
instanceofto check whether an object inherits from a constructor’s prototype (classes and constructor functions). - Beware:
typeof null === 'object'(historical bug). Do not useinstanceoffor primitives.instanceofcan be broken by multiple realms (iframes) or by customSymbol.hasInstancebehavior. - For arrays: use
Array.isArray(value). - For robust general type detection: use
Object.prototype.toString.call(value).
The operators at a glance
typeof x: returns a string describing the type category for primitives and some built-ins. See MDN: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/typeofx instanceof Ctor: returns true ifCtor.prototypeexists inx’s prototype chain (subject toSymbol.hasInstance). See MDN: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/instanceof
Deep dive: typeof - strengths and gotchas
What it does: typeof examines the type tag of a value and returns one of a small set of strings like 'string', 'number', 'boolean', 'undefined', 'symbol', 'bigint', 'function', or 'object'.
Example:
typeof 'hello'; // 'string'
typeof 42; // 'number'
typeof true; // 'boolean'
typeof undefined; // 'undefined'
typeof Symbol(); // 'symbol'
typeof 10n; // 'bigint'
typeof function () {}; // 'function'Important gotchas:
typeof null === 'object'- a long-standing quirk in JS. Do not rely ontypeofto detectnull.
typeof null; // 'object' <-- surprising- Arrays and plain objects both return
'object'withtypeof.
typeof []; // 'object'
typeof {}; // 'object'NaNis a number:typeof NaN === 'number'. UseNumber.isNaN(value)to test for NaN reliably.
typeof NaN; // 'number'
Number.isNaN(NaN); // true
NaN === NaN; // falseWhy typeof is great:
- Fast and reliable for primitives.
- Safe to call on any value (no exceptions).
When not to use it:
- When you need to distinguish between different object types (Array vs Object vs Date).
Deep dive: instanceof - what it checks and when it fails
What it does: obj instanceof Ctor returns true when Ctor.prototype appears in obj’s prototype chain. It’s for testing