· tips · 5 min read
The Power of the Nullish Coalescing Operator: Beyond Default Values
Learn how the nullish coalescing operator (??) helps you avoid common pitfalls with falsy values in JavaScript. Examples, gotchas, interactions with optional chaining and logical operators, TypeScript notes, and best practices included.
Why the nullish coalescing operator matters
When you want a fallback value in JavaScript, a common pattern has been to use the logical OR operator (||):
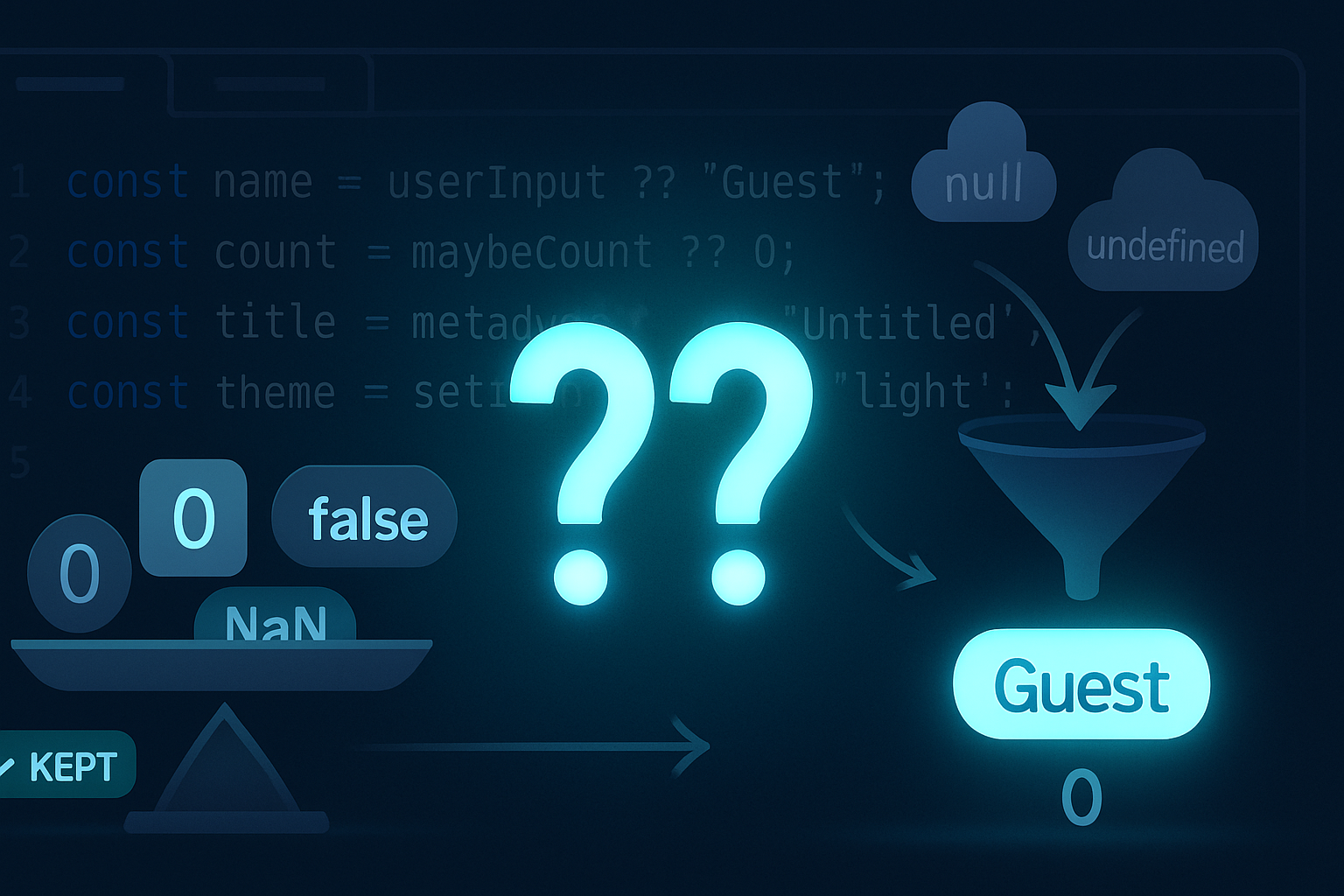
const name = userInput || 'Guest';That works - but it treats all falsy values the same. If userInput is '', 0, or false, you’ll get 'Guest' instead of the meaningful falsy value. The nullish coalescing operator (??) was introduced in ES2020 to address this: it only falls back when the left-hand side is null or undefined, not for other falsy values.
const name = userInput ?? 'Guest';name will be 'Guest' only if userInput is null or undefined.
(See the MDN reference: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Nullish_coalescing_operator)
The exact difference: || vs ??
||returns the right-hand side when the left-hand side is falsy (false,0,'',NaN,null,undefined).??returns the right-hand side only when the left-hand side is nullish (nullorundefined).
Examples:
console.log(0 || 10); // 10
console.log(0 ?? 10); // 0
console.log('' || 'default'); // 'default'
console.log('' ?? 'default'); // ''
console.log(null || 'fallback'); // 'fallback'
console.log(null ?? 'fallback'); // 'fallback'Note: NaN is not null or undefined, so NaN ?? 5 returns NaN.
Practical examples
- Preserving numerical zero
function formatCount(count) {
// We want to show 0 instead of default
const safeCount = count ?? 0;
return `You have ${safeCount} items`;
}
formatCount(0); // "You have 0 items"
formatCount(null); // "You have 0 items"
formatCount(); // "You have 0 items"- Allowing empty strings
function displayTitle(title) {
const safeTitle = title ?? 'Untitled';
// Intentionally allow '' (empty string) to be used
console.log(safeTitle);
}
displayTitle('Hello'); // 'Hello'
displayTitle(''); // ''
displayTitle(null); // 'Untitled'- With functions (short-circuiting)
const val = maybeGetValue() ?? computeExpensiveFallback();
// computeExpensiveFallback() is only called if maybeGetValue() returned null/undefined?? short-circuits like other logical operators: the right-hand side is evaluated only if needed.
Optional chaining + nullish coalescing: a powerful combo
Optional chaining (?.) and ?? are a natural pair for safely reading nested data with fallbacks:
const username = user?.profile?.username ?? 'Guest';This will return 'Guest' when user or profile is null/undefined, but will preserve empty strings or false if those are present.
(See MDN on optional chaining: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Optional_chaining)
Destructuring defaults vs ??
Default values in destructuring only apply when a property is undefined, not when it is null:
const obj = { count: null };
const { count = 10 } = obj;
console.log(count); // null (default not used)
// If you want to treat both null and undefined as missing:
const count2 = obj.count ?? 10;
console.log(count2); // 10If you prefer a destructuring-style shorthand that treats null as missing, combine destructuring with ??:
const obj = { count: null };
const { count } = obj;
const safeCount = count ?? 10; // 10Logical nullish assignment (??=) and friends
ES2021 introduced logical assignment operators that parallel ||= and &&=. ??= assigns only if the left-hand side is null or undefined:
let options = { retries: 0 };
options.retries ??= 3;
console.log(options.retries); // 0 (preserved)
let settings = {};
settings.retries ??= 3;
console.log(settings.retries); // 3 (assigned because undefined)Mixing with || and &&: the parentheses requirement
For safety and clarity, JavaScript disallows mixing ?? with || or && without parentheses. This is to avoid ambiguous expressions due to differences in how operators treat operands.
These are invalid syntax and will throw:
// SyntaxError:
// const x = a || b ?? c;
// const y = a && b ?? c;Use parentheses to make your intent explicit:
const x1 = (a || b) ?? c;
const x2 = a || (b ?? c);Think about the precedence and the meaning you want when combining these operators.
TypeScript and typing considerations
TypeScript supports ?? (added in TS 3.7). With --strictNullChecks, ?? helps reduce boilerplate when dealing with T | null | undefined types:
function greet(name: string | null | undefined) {
const who = name ?? 'friend';
// who is typed as string here
}Note: TypeScript’s control-flow analysis understands ?? to narrow types in many cases, but you should still be mindful when interacting with complex union types.
Browser / runtime support
?? was added in ES2020 and is supported in modern browsers and Node versions. If you need to target older environments, transpile with Babel or TypeScript. Check compatibility here: https://caniuse.com/mdn-javascript_operators_nullish_coalescing
Common pitfalls and gotchas
- Mistaking
nullishforfalsy:0,'',false, andNaNare falsy but not nullish. Use??when you need to preserve these values. - Mixing
??with||/&&without parentheses causes a syntax error. - Using
??where you actually want any falsy value to trigger fallback: e.g., when a missing/empty string should be replaced with a default,||may be appropriate. - Be explicit when expressing intent. If a field can legitimately be
nulland that should be replaced,??is correct. If a field can be0orfalseand those are meaningful, avoid||.
Best practices
- Use
??when you want to treat onlynullandundefinedas missing values. - Prefer explicit parentheses when combining logical operators to make precedence and intent obvious.
- Combine
?.and??for safe property access with sensible fallbacks. - Use logical nullish assignment (
??=) to initialize values without overwriting meaningful falsy data. - When working in teams, document intent: is an empty string a valid value or should it be replaced?
Quick reference cheat-sheet
- Use
x ?? yto getxunlessxisnullorundefined, otherwisey. - Use
x || yto getxunlessxis falsy (0,'',false,NaN,null,undefined). - Use
a ??= bto assignbtoaonly ifaisnullorundefined. - Use
?.and??together to safely read deep properties with defaults.
Summary
The nullish coalescing operator (??) is a small but powerful addition to JavaScript. It helps you write clearer, less error-prone code when you want to provide fallbacks for null and undefined but preserve other falsy values like 0, '', and false. Paired with optional chaining, destructuring, and logical assignment operators, ?? reduces boilerplate and makes intent explicit.
References
- MDN: Nullish coalescing operator: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Nullish_coalescing_operator
- MDN: Optional chaining: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Optional_chaining
- MDN: Logical nullish assignment: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Logical_nullish_assignment
- Destructuring defaults: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Destructuring_assignment#default_values
- Browser support (caniuse): https://caniuse.com/mdn-javascript_operators_nullish_coalescing